Monthly Case from the Department of Medicine
The Brainstem and Chronic Kidney Disease
Submitted by:
Liliana Guevara-Bermudez, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Emory University School of Medicine
Department of Medicine
Division of Hospital Medicine
Aurangzeb Memon, MD
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Emory University School of Medicine
Department of Neurology
Edited by:
Mary Ann Kirkconnell Hall, MPH
Division of Hospital Medicine
STORY AND CASE:
A 32-year-old man with a past medical history of hypertension and stage IV chronic kidney disease (CKD) was brought to the hospital by emergency medical services after he was found unresponsive. His initial blood pressure was 266/166 mmHg in the ambulance.
Upon physical examination, the patient remained unresponsive, with occasional gaze deviation to the right. He was unable to follow commands. Computed tomography (CT) and CT angiography (CTA) of his head were performed due to concern for possible stroke, with no evidence of hemorrhage or large vessel occlusion seen. He had elevated troponins as well as possible ischemic changes on electrocardiogram, both of which were believed to be due to demand ischemia from severe hypertension.
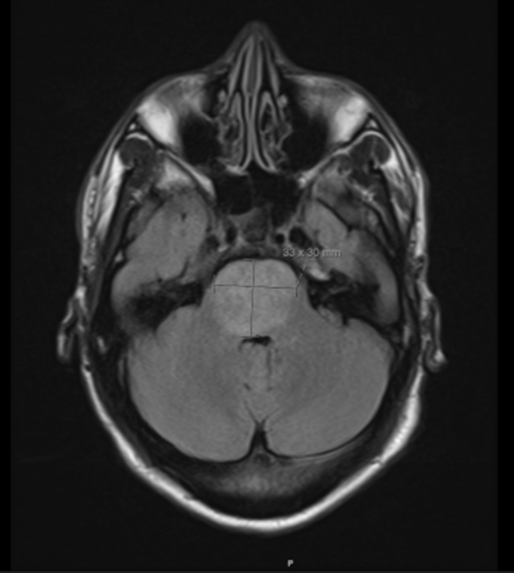
He was admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with acute on chronic kidney disease requiring emergent dialysis. He exhibited occasional head nodding, with electroencephalogram being negative for epileptiform discharges. Uremic encephalopathy was on the differential, and the patient was initiated on hemodialysis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of his brain with and without contrast showed pontine enlargement with diffuse T2 hyperintensity throughout the pons, with no evidence of restricted diffusion on diffusion-weighted imaging/apparent diffusion coefficient.
Figure 1: Initial Brain MRI
What’s the Diagnosis?
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES).
He was diagnosed with posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). PRES is a clinical radiological syndrome, characterized by a reversible vasogenic edema predominantly within parieto-occipital regions. Patients with autoimmune conditions, chronic renal dysfunction, and uncontrolled hypertension are at elevated risk for PRES. Patients with PRES can present with altered consciousness, vision changes, headaches, and seizures. PRES could be the first presentation of a condition such as CKD and hypertension; we report a combination of both. MRI scan is the preferred diagnostic tool for defining PRES. Early diagnosis is important since complete remission can be achieved after appropriate treatment.
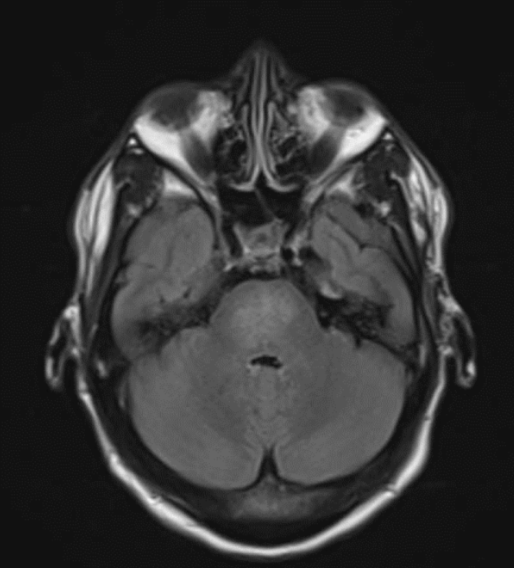
In this case, the patient’s blood pressure was aggressively controlled with a continuous nicardipine infusion in the ICU, and a neurology consult was obtained. A repeat brain MRI obtained eight days later showed partial resolution of the T2 hyperintensities observed in the pons.
Figure 2. MRI Brain, eight days later
Discussion:
A variety of etiologies for PRES have been reported, but the underlying mechanism is thought to be failed cerebral autoregulation. Isolated brainstem involvement in PRES is rarely seen or reported in clinical practice. Prior to proceeding with, and in an effort to avoid an invasive workup for brainstem abnormalities seen on MRI, we suggest repeat imaging to assess for interval improvement in signal abnormalities previously seen on initial MRI in patients presenting with the appropriate clinical context.
Clinicians should recognize isolated PRES, which according to literature, is classically seen in patients with severe hypertension, especially combined with renal dysfunction. When patients present with altered mental status, preliminary workup typically includes CT head without contrast to rule out stroke. However, among certain populations, other conditions should be higher on the differential than stroke.
Citations:
- Chiang, W. F., et al. (2019). “Atypical posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a noncompliant hemodialysis patient: Case report and literature review.” Hemodial Int 23(4): E100-e103.
- Ermeidi, E., et al. (2013). “Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a noteworthy syndrome in end-stage renal disease patients.” Nephron Clin Pract 123(3-4): 180-184.
- Forouzanfar, M., et al. (2014). “Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome as the first presentation of chronic kidney disease.” Am J Emerg Med 32(5): 489.e481-483.
- Gao, B., et al. (2012). “Isolated pons involvement in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a patient with chronic renal insufficiency: case report and literature review.” Clin Neuroradiol 22(4): 341-344.
- Hu, H., et al. (2017). “The clinical characteristics of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in patients with chronic renal failure.” Exp Ther Med 14(1): 881-887.


Be the first to comment on "Faculty Development Case of the Month: December 2023"